what does a dog see
Dogs are color blind
Where is the little red ball?
Tip: look through your dog's eyes yourself
Dogs see better in the dark
Dogs are born blind
During the first 10-14 days after birth, a puppy is deaf and blind. After this period - also called the neonatal stage - the eyes open and the closed ear canals also open.
Dogs are color blind
In order to perceive colors, there are special cells in the retina that catch light; so-called cones. Humans have 3 types of cones, each cone being sensitive to a different color: red, green and blue. With these 3 cones together, we are able to see everything in "full color. Dogs only have 2 types of cones and they also have fewer of them than we do. Therefore, they see fewer colors and the colors they see are less intense.
Scientific research
At the University of California, Jay Neitz did research on color blindness in dogs. He always showed dogs 3 light panels in a row, 2 of which were the same color. The dogs then had to point out the different color. If the answer was correct, the dog was rewarded. The results of this study show that dogs are particularly good at distinguishing the colors yellow and blue.
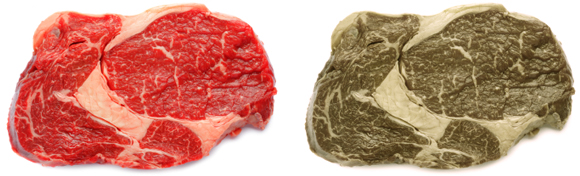
In the image below, you can see that orange, yellow and green are all somewhat similar; these colors and are perceived as a mustard yellow color by a dog. Red, like green, also resembles a brownish mustard color or sometimes even black. So dogs can hardly distinguish between red and green. Violet and blue merge, as it were, into the same shade of blue.
This is what a dog sees
Where is the red ball?
Many dog toys are red in color, but how does a dog see that? Since to dogs green and red are almost the same color, you can imagine that a red ball in the grass is not immediately noticeable to a dog.
Where is the red ball?
Dogs see better in the dark
Our dog's wild relatives and ancestors are/were active at dusk to hunt, so it is important for them to have good vision in the dark. Dogs still have this trait today. There are 3 reasons why dogs see better in the dark.
More rods
In the retina, in addition to cones, there are other light-sensitive cells: rods. Rods are very light-sensitive and allow us to see even in low light. Dogs have more rods than we do.
More light
In addition to the rods, there are 2 other parts of the eye that are important for the amount of light entering the eye: the cornea and the lens. The cornea - also called cornea - is the transparent part on the outside of the eye through which light enters. The lens is located behind the pupil
Dogs have a larger cornea than humans, allowing them to catch more light.
Tapetum lucidum
You've probably seen it on a cat in the dark or in a photo where flash is used: eyes of some animals light up in the dark as if they have lights in them. Behind the retina is a kind of mirror - the tapetum lucidum - it has a shiny surface and it reflects incoming light. In this way, incoming light can be put to extra use. Dogs also have a tapetum lucidum and therefore see better in the dark than we do.